
Adenosine will not terminate most atrial tachycardias but will temporarily increase the degree of AV block. Given in sufficient dosage (6–24 mg), adenosine will always terminate SVT with the exception of atrial tachycardia (see above).
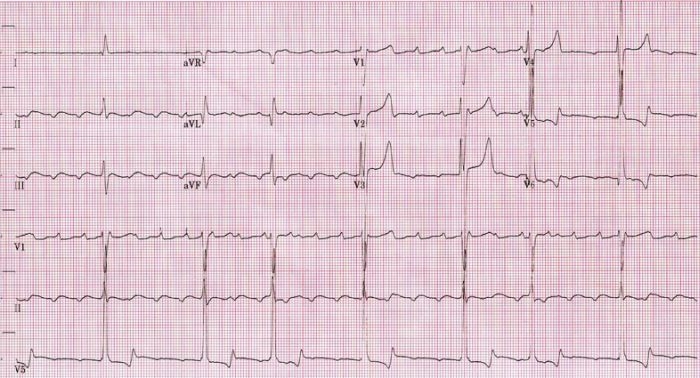
If vagal manoeuvres are ineffective, adenosine is the agent of choice. Vagal manoeuvres should be tried initially. It is uncommon for brief episodes of supraventricular arrhythmia to cause significant compromise to mother or fetus in the absence of structural cardiac disease. Pregnant women with documented sustained or frequent arrhythmia, recurrent palpitations or syncope should be assessed by a cardiologist. Diagnostic electrophysiological and tilt-table testing are rarely indicated in pregnancy. If symptoms are exacerbated by exercise an exercise stress test can be useful.

Unless the symptoms are occurring daily, the Holter recording is often inconclusive. Contributing metabolic disorders should be excluded.Ī baseline ECG must be obtained and the patient should be considered for a 24-hour ECG Holter monitor and echocardiogram. Tachyarrhythmias can be caused or exacerbated by hyperthyroidism. A family history of sudden death or structural heart disease is important. History of structural heart disease, exacerbating situations, exercise capacity, a description of arrhythmia onset and termination as well as any associated symptoms, especially syncope, should be sought. A thorough history and examination are essential. Many women experience the sensation of palpitations during pregnancy. 8 Arrhythmias of haemodynamic significance during labour are surprisingly rare.
#Atrial flutter causes during pregnancy series#
One large retrospective series found that only 0.17% of hospital admissions during pregnancy were for cardiac arrhythmia and for every 100,000 pregnant women, 24 will be admitted for management of supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) (Figure 1), two with atrial fibrillation (AF), two with ventricular tachycardia (VT) (Figure 2) or fibrillation and 1.5 with atrioventricular (AV) block. Frequent ventricular ectopics can sometimes indicate underlying heart disease and further investigation may be warranted. 7 Although sometimes annoying, in general they are benign in structurally normal hearts and usually do not require treatment. 7 For many women, pregnancy is a time of heightened awareness and it is likely that increased heart rate and stroke volume contribute to the sensation of a ‘pounding heart’ that at times is perceived as palpitations.īenign atrial and ventricular ectopic beats are more frequent during pregnancy. Palpitations are frequently reported during pregnancy however these symptoms often do not correspond to episodes of arrhythmia on 24-hour ECG Holter monitoring. 1ĭOES THE INCIDENCE OF CARDIAC ARRHYTHMIAS INCREASE DURING PREGNANCY? Adequate analgesia can substantially attenuate the haemodynamic changes. Immediately after delivery, relief of caval compression as well as autotransfusion from the uterus can cause a significant increase in blood volume despite the fluid losses in labour. Anxiety, pain and uterine contractions all contribute.

4ĭuring labour, cardiac output rises substantially due to both a rise in heart rate and stroke volume. 3 The increased sympathetic outflow that occurs in pregnancy probably also contributes to the proarrhythmic milieu. The normal adjustment in sex hormones that occurs during pregnancy may exert a proarrhythmic effect on myocardial tissue. 2 The rise in heart rate can be marked, especially in the multigravida pregnancy. Later in pregnancy a rise in heart rate, on average 20 beats per minute, accounts for further enhancement in cardiac output. The increase in blood volume can cause atrial stretch that may be significant for arrhythmogenesis.
This is largely due to an expanding stroke volume that plateaus at around 24 weeks gestation. 1 Cardiac output rises by about 50% with a steep increase from the latter half of the first trimester. The systolic pressure usually returns to near pre-gestational levels by term. Blood pressure usually falls, reaching a nadir in mid-pregnancy. CARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY AND ARRHYTHMOGENESIS DURING PREGNANCY AND LABOURīlood volume increases by an average of 50% during pregnancy.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
